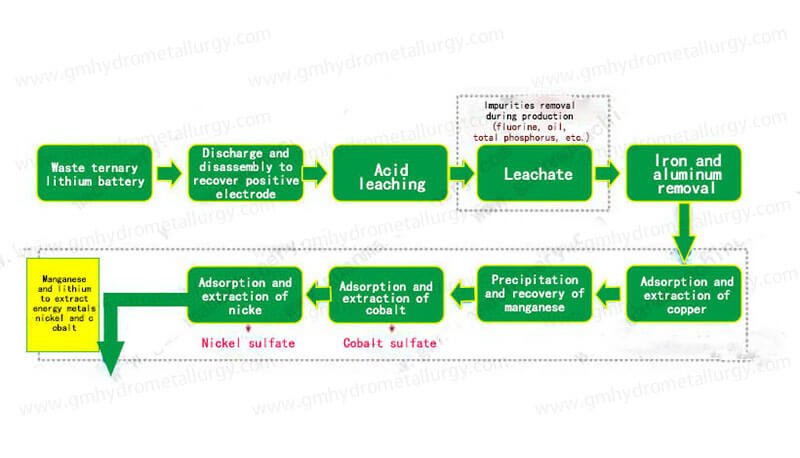
Hydrometallurgy is a versatile and increasingly important branch of extractive metallurgy that involves the use of aqueous chemistry to recover metals from ores, concentrates, and other feedstocks. This process is particularly significant in the recycling of metals, especially in the context of lithium-ion battery recycling. In this article, we will explore the metals that can be extracted through hydrometallurgy, with a focus on the lithium-ion battery recycling process, and discuss the key steps and equipment involved in the hydrometallurgy process.
Introduction to Hydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy is a method of extracting and purifying metals from ores and other materials using aqueous solutions. Unlike pyrometallurgy, which relies on high temperatures, hydrometallurgy operates at lower temperatures and pressures, making it more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. The process typically involves leaching, precipitation, and solvent extraction techniques to isolate and purify the desired metals.
Metals Extracted by Hydrometallurgy
1. Copper (Cu):
Copper is one of the most commonly extracted metals using hydrometallurgy. It is often recovered from low-grade ores and mine tailings through heap leaching, where sulfuric acid is used to dissolve the copper from the ore.
2. Gold (Au):
Gold can be extracted from ores and electronic waste using cyanide leaching. The gold forms a soluble complex with cyanide ions, which can then be recovered through electrowinning or precipitation with zinc.
3. Nickel (Ni):
Nickel is extracted from laterite ores and spent catalysts using pressure leaching with sulfuric acid. The nickel is then recovered through solvent extraction and electrowinning.
4. Zinc (Zn):
Zinc is often extracted from sphalerite ores using the zinc roasting and leaching process. The zinc oxide is leached with sulfuric acid, and the zinc is recovered through electrowinning.
5. Lithium (Li):
Lithium is a critical component of lithium-ion batteries and is increasingly extracted from brines and ores using hydrometallurgical processes. The lithium is leached from the feedstock using a variety of lixiviants, and it is then purified through solvent extraction and precipitation.
Key Equipment in the Hydrometallurgy Process
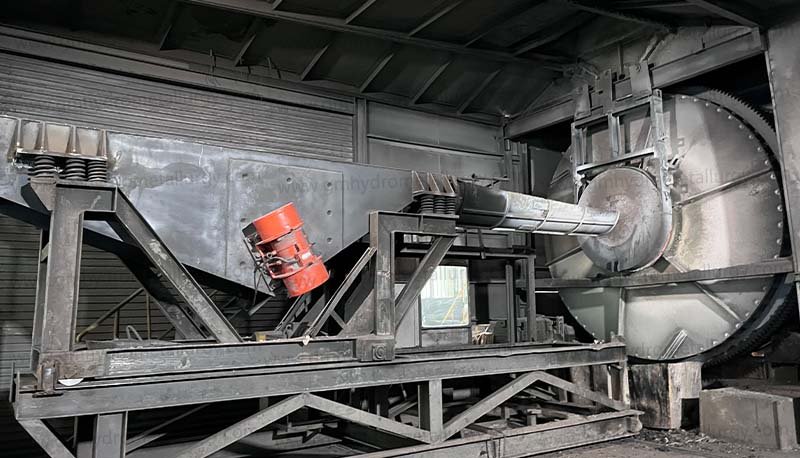
1. Shredders and Crushers
These machines are used to break down the batteries into smaller pieces, increasing the surface area for leaching.
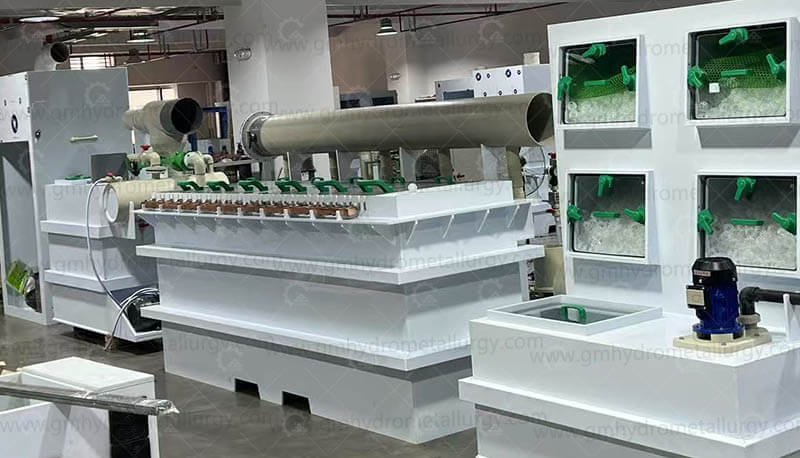
2. Leaching Tanks
Leaching tanks are used to mix the battery materials with the lixiviant solution. They are designed to optimize the leaching process by controlling factors such as temperature, pH, and agitation.
3. Solvent Extraction Units
Solvent extraction units are used to separate the metals from the leachate. They typically consist of mixing and settling stages to ensure efficient extraction.
4. Electrowinning Cells
Electrowinning cells are used to deposit the metals onto a cathode. They are equipped with electrodes and a power supply to facilitate the electrochemical deposition process.
5. Filtration and Drying Systems
Filtration and drying systems are used to separate the precipitated metals from the solution and to dry the metal compounds for storage and transportation.
Benefits of Hydrometallurgy in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling
Resource Recovery
Hydrometallurgy allows for the efficient recovery of valuable metals from lithium-ion batteries, reducing the need for primary mining and conserving natural resources.
Environmental Impact
The process is more environmentally friendly compared to traditional pyrometallurgical methods, as it operates at lower temperatures and produces fewer emissions.
Economic Viability
The recovery of high-value metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel makes the recycling process economically viable, creating new business opportunities and reducing waste.
Hydrometallurgy is a powerful and versatile technique for extracting metals from various feedstocks, including lithium-ion batteries. The process offers numerous benefits, including resource recovery, environmental sustainability, and economic viability. By understanding the key steps and equipment involved in the hydrometallurgy process, businesses and researchers can optimize their recycling operations and contribute to a more sustainable future.
If you are interested in learning more about the latest advancements in hydrometallurgy and Lithium-ion battery recycling, or if you need specialized equipment for your recycling operations, feel free to contact us. We are committed to providing you with the best solutions and support to meet your needs.