Hydrometallurgical Recycling of Lithium
In the rapidly evolving world of renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs), lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are at the heart of the transition. However, with an increasing number of batteries reaching end-of-life, sustainable disposal and recovery solutions have become critical. This is where hydrometallurgical recycling of lithium comes into play—a highly efficient, eco-friendly method for extracting valuable metals from used batteries.
How Does the Hydrometallurgical Recycling Process Work?
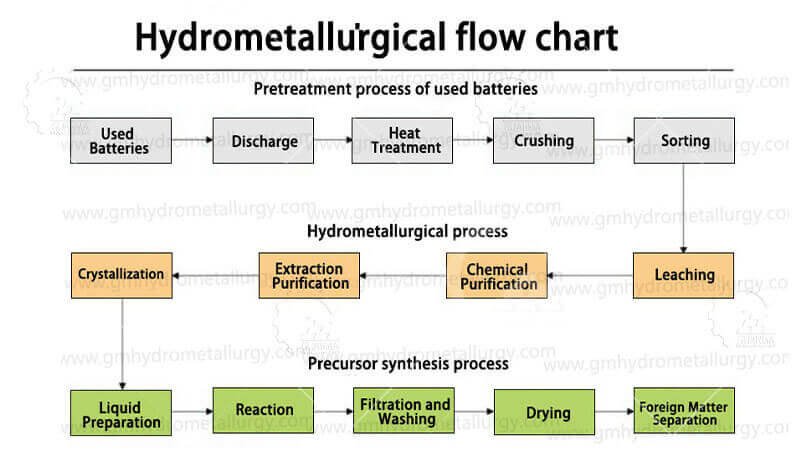
Unlike traditional methods like pyrometallurgy, which involves high-temperature smelting, hydrometallurgical recycling uses aqueous chemistry to recover materials. The process typically involves several detailed steps:
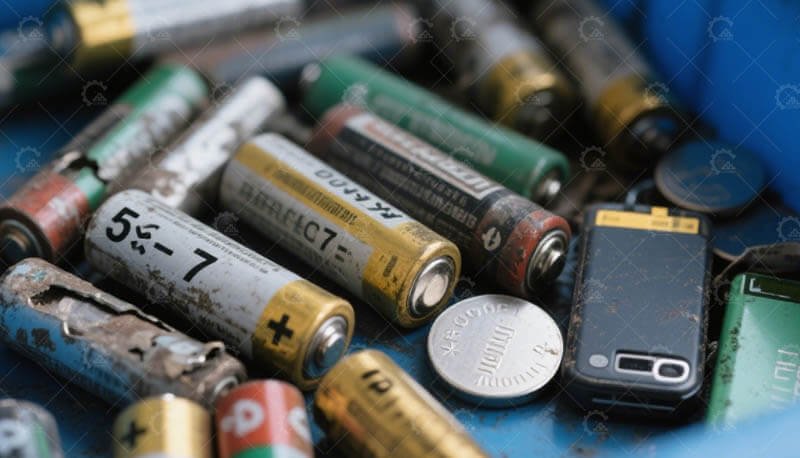
1. Battery Collection and Pre-processing
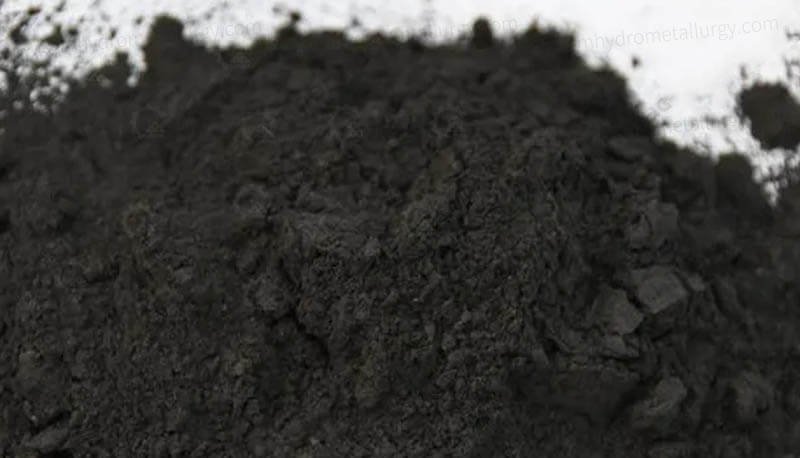
Spent lithium-ion batteries are collected, discharged, and dismantled. The components are then shredded to create a homogeneous powder known as “black mass.”
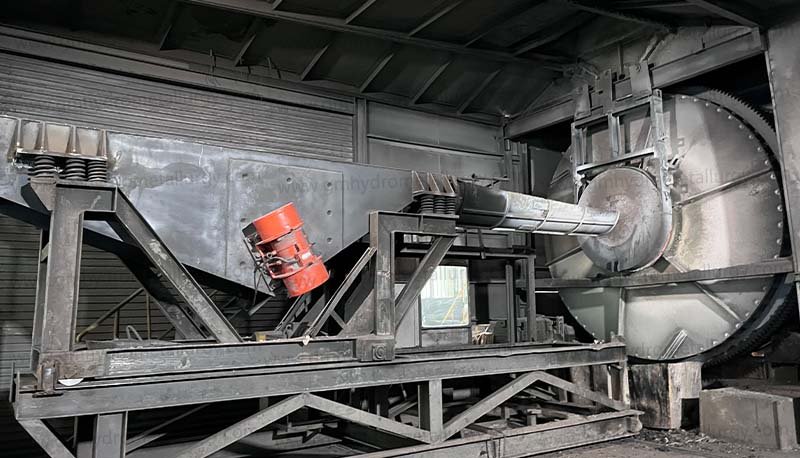
2. Leaching
The black mass is treated with chemical solutions (acids or bases) to dissolve the valuable metals into a liquid phase. Commonly used reagents include sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) or hydrochloric acid (HCl), which help leach lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese.
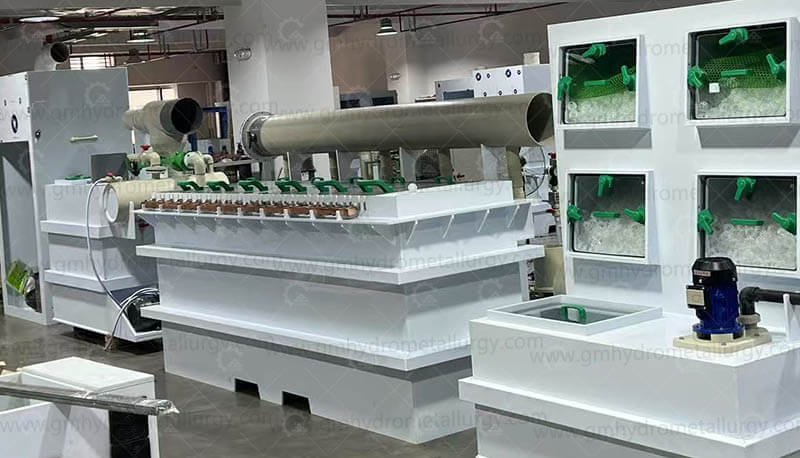
3. Purification and Separation
The leachate undergoes multiple purification steps to remove impurities. Techniques such as precipitation, solvent extraction, or ion exchange are employed to isolate individual elements. For instance, cobalt can be separated using selective precipitation, while lithium is often recovered as lithium carbonate.
4. Recovery of High-Purity Materials
The purified solutions are processed to obtain high-purity metal salts or compounds. Lithium is typically precipitated as lithium carbonate (Li₂CO₃) or lithium hydroxide (LiOH), which are directly usable in new battery production.
Why Choose Hydrometallurgical Recycling?
Higher Recovery Rates
This method achieves recovery rates of over 90% for key metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, far surpassing pyrometallurgical techniques.
Environmental Benefits
It operates at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, it minimizes hazardous waste generation.
Economic Value
By providing a secondary source of critical materials, it mitigates supply chain risks and reduces dependency on mining.
For businesses involved in battery manufacturing, EV production, or waste management, integrating hydrometallurgical recycling of lithium-ion batteries can be a game-changer. This process supports sustainable lithium recovery and aligns with circular economy goals. Moreover, it offers a cost-effective lithium extraction method while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
The Future of Battery Recycling
As global demand for lithium continues to soar, hydrometallurgical recycling presents a scalable and efficient solution. For companies looking to secure a sustainable supply chain, investing in or partnering with recycling facilities using this technology is a strategic move. Not only does it promote environmental stewardship, but it also enhances economic resilience.